
IMPORTANT: when inserting an Expression in an object, you will need to assign one of the Tags managed in the expression as the object's contextual Tag.
Movicon.NExT Help on Line - Rel. 4.2.358
It is possible to insert expressions or formulae in the object's 'Expressions' and 'Inverse Expressions' property fields (or Animation properties).
This possibility enables the system to calculate the set expression and display the result as an assigned object value.
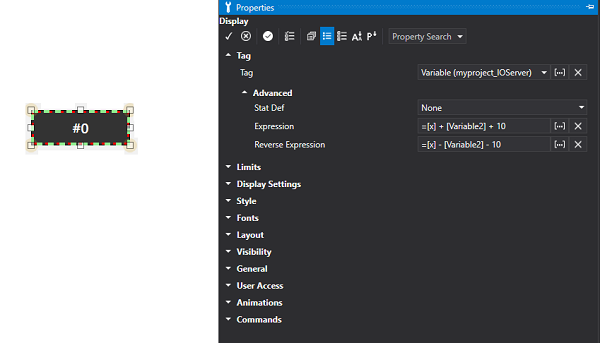
Expressions in objects
If you wish to show the resulting value from an expression between a Tag and a constant calculation in the Display, you will need to assign the Tag to the object as a Contextual Tag and then insert the calculation expression in the Display's 'Expression' property. From this point onwards, the Display will no longer display the Tag value but the resulting expression's value at runtime.
|
IMPORTANT: when inserting an Expression in an object, you will need to assign one of the Tags managed in the expression as the object's contextual Tag. |
In cases in which the object, for example the Display object, should be editable, it will be necessary to insert the 'Inverse Expression' by means of which the value's bidirectionality can be managed. When the control is also editable, it is necessary to retrieve the value with which to set the variable associated to the object when the control is edited.
For example, associating the "TagName1" variable to a Display object and then inserting the following formula in the "Expression" field:
=[x] + [TagName2] + 10
Where the placeholder "[x]" represents the value of the contextual Tag associated to the control. The square brackets, however, are used to indicate that the content is a Movicon.NExT variable. .
At this point, if the dynamic value of the “TagName1” associated to the Display object is 1, and the value of the “TagName2” is 2, the displayed value will be the result of the expression being:
1 +2 + 10 = 13
If the Display is also editable, it will be necessary to apply the inverse formula to set the variable according to the inserted value. In this case, the 'Inverse Expression' field should be edited with the following formula:
=[x] - [TagName2] - 10
Where, in this case, the placeholder [x] represents the value inserted in the display object (and not the value of the Contextual Tag) and the result of the formula is then inserted in the contextual Tag associated to the object, for example "TagName1".
At this point, if the value inserted in the Display is 20 and the value of the 'TagName' is 2, the 'TagName1' will be set with the resulting value of the expression:
20 - 2 - 10 = 8
|
The inverse expression is valued only when the direct Expression has been inserted. Otherwise the Inverse Expression will be ignored.
|
To realize the above described example, please proceed as follows:
Open a screen and insert an object such as the Display object.
Assign the “TagName1” variable to the Display to use as the Display's Contextual Tag.
Insert the expression with the =[x] + [TagName2] + 10 syntax in the Display's 'Expression' property.
Insert the expression with the =[x] - [TagName2] - 10 syntax in the Display's 'Inverse Expression' property.
The Display will display the result of the expression at project runtime.
Object Tooltip commands are used for inserting expressions or formulae for displaying data.
|
Warning! A localization problem in converting double values currently exists. To remedy this problem for the time being you will need to set the English language in your local workstation in order to test expressions. |
|
Attention! The expression manager does not recognize variable names as "Case Sensitive". Therefore, the expression might not be valued correctly if more than one variable has the same name which is distinguished by uppercase or lowercase letters (e.g. "TankLevel" and "tanklevel"). |
The functions and syntaxes available for the expressions are Ms Excel 2013 type and permit mathematical and logic combinations with project tags.
This editor window will help you compose complex expressions.
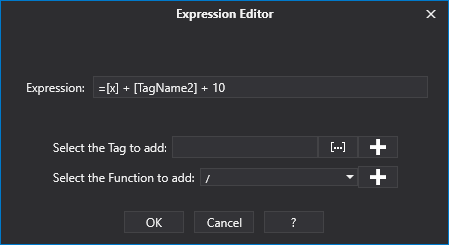
Variable or formulae and functions can be added to the expression field by selecting them from the drop-down list indicated by the down pointed arrows on the right. After selecting the ones desired use the "Add" button to add them to the Expression field above.
|
Warning! If a decimal value is inserted in the expression (eg 1.3 etc.) it will be necessary to use the dot (".") as decimal separator, independently from the Windows settings (eg: = [x] + [TagName2] + 1.3). |
List of functions that can be used in Expressions
Function |
Syntax |
Description |
ABS |
ABS(number) |
Returns the absolute value of a number. The absolute value of a non-negative number is the number itself. The absolute value of a negative number is -1 times the number.
|
ACCRINT |
ACCRINT(issue, first_interest, settlement, rate, par, frequency, [basis], [calc_method]) |
Returns the accrued interest for a security that pays periodic interest on a periodic basis.
|
ACOS |
ACOS(number) |
Returns the inverse cosine of a number. Inverse cosine is also referred to as arccosine. The arccosine is the angle whose cosine is the given number. The returned angle is given in radians in the range of 0 to pi.
|
ACOSH |
ACOSH(number) |
Returns the inverse hyperbolic cosine of a number. The number must be greater than or equal to 1. The inverse hyperbolic cosine is the value whose hyperbolic cosine is the given number.
|
ACOT |
ACOT(number) |
Retrieves the principal value of the inverse trigonometric cotangent of a number.
|
ACOTH |
ACOTH(number) |
Retrieves the inverse hyperbolic cotangent of a number.
|
ACSCH |
ACSCH(number)
|
Returns the inverse hyperbolic cosecant |
AND |
AND(logical1, logical2, ...) |
Returns True if all the arguments have a logical value of True and returns False if at least one argument is False.
|
ARABIC |
ARABIC( romannumeral ) |
A Roman numeral is converted into an Arabic numeral.
|
ASC |
ASC(text) |
The ASC function used to convert full-width (double-byte) characters to half-width (single-byte) characters.
|
ASECH |
Y = ASECH(X) |
Inverse hyperbolic secant
|
ASIN |
ASIN(number) |
Returns the inverse sine of a number. Inverse sine is also referred to as arcsine. The arcsine is the angle whose sine is the given number. The returned angle is given in radians in the range from -pi/2 to +pi/2.
|
ASINH |
ASINH(number) |
Returns the inverse hyperbolic sine of a number. The inverse hyperbolic sine is the value whose hyperbolic sine is the given number, so ASINH(SINH(number)) equals number.
|
ATAN |
ATAN(number) |
Returns the inverse tangent of a number. Inverse tangent is also known as arctangent. The arctangent is the angle whose tangent is a number. The returned angle is given in radians in the range from -pi/2 to +pi/2.
|
ATAN2 |
ATAN2(x_num,y_num) |
Returns the inverse tangent of the specified x and y co-ordinates. The arctangent is the angle from the x-axis to a line containing the origin (0, 0) and the point (x_num, y_num). The angle is given in radians between -pi and pi, excluding -pi.
|
ATANH |
ATANH(number) |
Returns the inverse hyperbolic tangent of a number. Number must be strictly between -1 and 1. The inverse hyperbolic tangent is the value whose hyperbolic tangent is number, so ATANH(TANH(number)) equals the given number.
|
AVEDEV |
AVEDEV(number1, number2, ...) |
Returns the average of the absolute mean deviations of data points. AVEDEV is a measure of the variability in a data set.
|
AVERAGE |
AVERAGE(number1, number2, ...) |
Returns the average (arithmetic mean) of the arguments.
|
AVERAGEA |
AVERAGEA(value1, value2,...) |
Calculates the average (arithmetic mean) of the values in the list of arguments. In addition to numbers and text logical values such as True and False are also included in the calculation.
|
AVG |
AVG(number1, number2,...) |
Returns the average (arithmetic mean) of the arguments.
|
BINOMDIST |
BINOMDIST(number_s, trials, probability_s, cumulative)
|
Returns the individual term binomial distribution probability. |
Base |
BASE(number, radix, [min_length]) |
The BASE function converts a number into a text representation with the given radix (base).
|
Besseli |
BESSELI(X, N) |
Returns the modified Bessel function In(X), which is equivalent to the Bessel function evaluated for purely imaginary arguments.
|
Besselij |
BESSELJ( X, N ) |
Returns the Bessel function Jn(X).
|
Besselk |
BESSELK( X, N ) |
Returns the modified Bessel function Kn(X), which is equivalent to the Bessel function evaluated for purely imaginary arguments.
|
BesselY |
BESSELY( X, N ) |
Returns the Bessel function Yn(X).
|
BETA.DIST |
BETA.DIST(x,alpha,beta,cumulative,[A],[B]) |
Calculates the cumulative beta distribution function or the probability density function of the Beta distribution, for a given set of parameters.
|
Bigmul |
BIGMUL(number1,number2)
|
Returns the complete product of two numbers
|
BIN2DEC |
BIN2DEC(number) |
The BIN2DEC function converts a binary number into a decimal number.
|
BIN2HEX |
BIN2HEX(number places)
|
The BIN2HEX function converts a binary number into a hexadecimal.
|
bin2oct |
BIN2OCT(num, places) |
The BIN2OCT function converts a binary number into an octal number.
|
Binom.Dist |
BINOM.DIST (trial number,sp,value, cumulative) |
The Binom.Dist function returns the Binomial Distribution probability for a given number of successes from a specified number of trials.
|
Binom.inv |
BINOM.INV(trial number,sp,value) |
The Binom.Inv function returns the smallest value for which the cumulative binomial distribution is greater than or equal to a criterion value.
|
BINOMdist |
BINOMDIST(number_s,trials,probability_s,cumulative) |
Returns the individual term binomial distribution probability.
|
BItand |
BITAND(expr1, expr2) |
Returns the output as bitwise AND of the inputs, the inputs, and its output are treats as vectors of bits.
|
Bitlshift |
BITLSHIFT(num1,num2) |
The BITLSHIFT function returns a number shifted left by specified number of bits.
|
bitor |
BITOR(num1, num2) |
The BITOR function returns a bitwise ‘OR’ of two numbers.
|
bitrshift |
BITRSHIFT(num1,num2) |
The BITRSHIFT function returns a number shifted right by the specified number of bits.
|
bitxor |
BITXOR(num1, num2) |
The BITXOR function returns bitwise XOR of two numbers. |
CEILING |
CEILING(number, significance) |
Returns number rounded up, away from zero, to the nearest multiple of significance. For example, if you want to avoid using pennies in your prices and your product is priced at $4.82, use the formula =CEILING(4.82,0.05) to round prices up to the nearest nickel.
|
CEILING.math
|
CEILING.MATH(number, [significance], [mode]) |
Rounds a number up to the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance. |
Char |
Char(number) |
The Char function returns the character whose number code is defined in the parameter.
|
CHIDIST |
CHIDIST(x, degrees_freedom) |
Returns the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution. The χ2 distribution is associated with a χ2 test.Use the χ2 test to compare observed and expected values.
|
CHIINV |
CHIINV(probability, degrees_freedom) |
Returns the inverse of the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared (χ2) distribution. If probability = CHIDIST(x,...), then CHIINV(probability,...) = x. Use this function to compare observed results with expected ones in order to decide whether your original hypothesis is valid.
|
CHIsq.dist |
CHISQ.DIST(x,degFreedom,cumulative) |
The Chisq.Dist function calculates the Probability Density Function or the Cumulative Distribution Function for the chi-square distribution.
|
CHIsq.dist.rt
|
CHISQ.DIST.RT(x,degFreedom) |
The Chisq.Dist.Rt function calculates the right-tailed probability of the chi-square distribution.
|
chisq.inv |
CHISQ.INV(probability,degFreedom) |
The Chisq.Inv function returns the inverse of the left-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution.
|
chisq.inv.rt |
CHISQ.INV.RT(probability, degFreedom) |
The Chisq.Inv.Rt function calculates the inverse of the right-tailed probability of the chi-square distribution.
|
CHIsq.TEST
|
CHISQ.TEST(actual_range,expected_range) |
Returns the chi-squared statistical test for independence
|
CHITEST |
CHITEST(actual_range, expected_range) |
Returns the test for independence. CHITEST returns the value from the chi-squared (c2) distribution for the statistic and the appropriate degrees of freedom.
|
Clean |
CLEAN(Text) |
The Clean function is used to remove the non-printable characters from the given text, represented by numbers 0 to 31 of the 7-bit ASCII code.
|
code |
CODE(name) |
The Code function converts the first character of a supplied text string into a numeric character set code.
|
Choose |
Choose(index, valuearray) |
The Choose function returns the value from a range of values on a specific index.
|
Column |
Column(range) |
The Column function returns the column index of the provided column in range.
|
COMBIN |
COMBIN(number, number_chosen) |
Returns the number of combinations for a given number of items. Use COMBIN to determine the total possible number of groups for a given number of items.
|
COMBINa |
COMBINA(number1, number2) |
For a given number of items, the Combina function returns the number of combinations.
|
complex |
COMPLEX(real_num, i_num, [suffix]) |
The function COMPLEX converts user-supplied real and imaginary coefficients into a complex number
|
CONCATENATE |
CONCATENATE (text1, text2,...) |
Joins several text strings into one text string.
|
CONFIDENCE |
CONFIDENCE(alpha,standard_dev,size) |
Returns a value that you can use to construct a confidence interval about a population mean. The confidence interval is a range of values. In your sample, mean x is at the center of this range and the range is x ± CONFIDENCE. For example, if x is the sample mean of delivery times for products ordered through the mail, x ± CONFIDENCE is a range of population means.
|
CONFIDENCE.norm |
CONFIDENCE.NORM(alpha,stdev,size) |
The Confidence.Norm function uses Normal Distribution to calculate a confidence value that can be used to construct the confidence interval for a population mean, for a supplied probability, and sample size.
|
CONFIDENCE.t
|
CONFIDENCE.T(alpha,standard_dev,size) |
Returns the confidence interval for a population mean
|
convert |
CONVERT(number,from_unit,to_unit) |
The function CONVERT converts a number from one measurement system to another.
|
CORREL |
CORREL(array1, array2) |
Returns the correlation coefficient of the array1 and array2 cell ranges.
|
COS |
COS(number) |
Returns the cosine of the given angle.
|
COSH |
COSH(number) |
Returns the hyperbolic cosine of a number.
|
cot |
COT(number) |
The Cot function returns the cotangent of an angle specified in radians.
|
coth |
COTH(number) |
The COTH function returns the hyperbolic cotangent of a hyperbolic angle.
|
COUNT |
COUNT(value1, value2,...) |
Counts the number of items in a list that contains numbers.
|
COUNTA |
COUNTA(value1, value2,...) |
Counts the number of cells that are not empty.
|
COUNTBLANK |
COUNTBLANK(range) |
Counts empty cells in a specified range of cells.
|
COUNTIF |
COUNTIF(range, criteria) |
Counts the number of cells within a range that meet the given criteria.
|
COVAR |
COVAR(array1, array2) |
Returns covariance, the average of the products of deviations for each data point pair.
|
COVARiance.p |
COVARIANCE.P(array1,array2) |
Returns population covariance, the average of the products deviation for each data point pair in two data sets.
|
COVARIANCE.S |
COVARIANCE.S(array1,array2) |
Returns the sample covariance, the average of the products deviation for each data point pair in two data sets.
|
CRITBINOM |
CRITBINOM(trials, probability_s, alpha) |
Returns the smallest value for which, the cumulative binomial distribution is greater than or equal to a criterion value.
|
csc |
CSC(number) |
The CSC function returns the cosecant of an angle specified in radians.
|
CSCh |
CSCH(number) |
The CSCH function returns the hyperbolic cosecant of an angle specified in radians.
|
Cumipmt |
CUMIPMT(rate, nper, pv, start_period, end_period, type) |
Calculates the cumulative interest paid between two specified periods.
|
cumprinc |
CUMPRINC(rate, nper, pv, start_period, end_period, type) |
Calculates the cumulative principal paid on a loan, between two specified periods.
|
DATE |
DATE(year, month, day) |
Returns the sequential serial number that represents a particular date.
|
DATEVALUE |
DATEVALUE(date_text) |
Returns the serial number of the date represented by the date_text.
|
DAY |
DAY(serial_number) |
Returns the day of a date, represented by a serial number. The day is given as an integer ranging from 1 to 31.
|
days |
DAYS(endDate, startDate) |
The Days function retrieves the number of days between two dates.
|
DAYS360 |
DAYS360(start_date, end_date, method) |
Returns the number of days between two dates based on a 360-day year (twelve 30-day months) which, is used in some accounting calculations.
|
DB |
DB(cost, salvage, life, period, month) |
Returns the depreciation of an asset for a specified period using the fixed-declining balance method.
|
dcount |
DCOUNT(database, field, criteria) |
Returns the number of cells containing numbers in a field of a list or database that satisfy specified conditions.
|
dcounta |
DCOUNTA(database, field, criteria) |
Returns the number of non-blank cells in a field of a list or database, that satisfy specified conditions.
|
DDB |
DDB(cost, salvage, life, period, factor) |
Returns the depreciation of an asset for a specified period using the double-declining balance method or some other method you specify.
|
dec2bin |
DEC2BIN(num,places) |
The DEC2BIN function converts a decimal number into a binary number.
|
dec2hex |
DEC2HEX(number, [places]) |
The DEC2HEX function converts a a decimal number to hexadecimal
|
dec2oct |
DEC2OCT(num, places) |
The DEC2OCT function converts a decimal number into an octal number.
|
decimal |
DECIMAL(text, radix) |
A text representation of a number in a given base to be converted into a decimal number.
|
DEGREES |
DEGREES(angle) |
Converts radians into degrees.
|
delta |
DELTA(number1, [number2]) |
The function DELTA tests whether two supplied numbers are equal.
|
DEVSQ |
DEVSQ(number1, number2,...) |
Returns the sum of squares of deviations of data points from their sample mean.
|
dget |
DGET(database, field, criteria) |
Returns a single value from a field of a list or database, that satisfy specified conditions.
|
disc |
DISC(settlement, maturity, pr, redemption, [basis]) |
It will calculate the rate of discount for a bond. It helps to know the discount rate when we know the other details about the bond.
|
divrem |
DivRem(int dividend, int divisor)
|
This method is used to calculate the quotient of two 32-bit signed integers.
|
dmax |
DMAX(database, field, criteria) |
Returns the largest number in a field (column) of records in a list or database that matches conditions you that specify.
|
dmin |
DMIN(database, field, criteria) |
Returns the smallest number in a field (column) of records in a list or database that matches conditions that you specify.
|
Dollar |
Dollar (number, decimal_places) |
The Dollar function converts a number to text, using a currency format. The format used is $#,##0.00_);($#,##0.00).
|
dollarde |
DOLLARDE(fractional-dollar, fraction) |
The DOLLARDE function is one of the financial functions. It is used to convert a dollar price represented as a fraction into a dollar price represented as a decimal number.
|
dollarfr |
DOLLARFR(decimal_dollar, fraction) |
DOLLARFR helps in converting a dollar value in decimal notation into a dollar value expressed in fractional notation.
|
dstdev |
DSTDEV(database, field, criteria) |
Estimates the standard deviation of a population based on a sample by using the numbers in a field (column) of records in a list or database that match conditions that you specify.
|
dstdevp |
DSTDEVP(database, field, criteria) |
Calculates the standard deviation (based on an entire population) of values in a field of a list or database, that satisfy specified conditions
|
dsum |
DSUM(database, field, criteria) |
Adds the numbers in the field (column) of records in a list or database that match the conditions you specify
|
duration |
DURATION(settlement, maturity, coupon, yld, frequency, [basis]) |
The DURATION function, one of the Financial functions, returns the Macauley duration for an assumed par value of $100. Duration is defined as the weighted average of the present value of cash flows, and is used as a measure of a bond price's response to changes in yield.
|
dvar |
DVAR(database, field, criteria) |
Calculates the variance (based on a sample of a population) of values in a field of a list or database, that satisfy specified conditions.
|
DVArp |
DVARP(database, field, criteria) |
Calculates the variance (based on an entire population) of values in a field of a list or database, that satisfy specified conditions.
|
Edate |
EDATE( startDate, Months ) |
The EDate function returns a date that is a specified number of months before or after a supplied start date.
|
encodeurl |
ENCODEURL(name) |
The EncodeURL function retrieves an URL-encoded string.
|
eomonth |
EOMONTH(startDate, Months) |
The EOMONTH function returns the last day of the month that is a specified number of months before or after an initially supplied start date.
|
erf |
ERF(lower_limit,[upper_limit]) |
The function ERF returns the error function integrated between two supplied limits |
ERF.PRECISE |
ERF.PRECISE(x) |
The function ERF.PRECISE returns the error function integrated between 0 and a supplied limit
|
ERFC.PRECISE |
ERFC.PRECISE(x) |
The function ERFC.PRECISE returns the complementary error function integrated between a supplied lower limit and infinity.
|
error.type |
= ERROR.TYPE(value) |
Error.Type function returns an integer for the given error value that denotes the type of given error.
|
EVEN |
EVEN(number) |
Returns the number rounded up to the nearest even integer.
|
Exact |
Exact(value1, value2) |
The Exact function compares two values ignoring the styles and returns the boolean value as true or false.
|
EXP |
EXP(number) |
Returns e raised to the power of the given number.
|
EXPON.DIST |
EXPON.DIST(x,y,cumulative) |
The Expon.Dist function calculates the value of the probability density function or the cumulative distribution function for the Exponential Distribution.
|
EXPONDIST |
EXPONDIST(x, lambda, cumulative) |
Returns the exponential distribution.
|
f.dist |
F.DIST(x,degFreedom1,degFreedom2,cumulative) |
The F.Dist function calculates the Probability Density Function or the Cumulative Distribution Function for the F Distribution.
|
F.DIST.RT |
F.DIST.RT(x, degFreedom1, degFreedom2) |
The F.Dist.Rt function calculates the F Probability Distribution that measures the degree of diversity between two data sets.
|
f.inv.rt |
F.INV.RT(probability,degFreedom1,degFreedom2) |
The F.INV.RT function calculates the inverse of the Cumulative F Distribution for a supplied probability.
|
FACT |
FACT(number) |
Returns the factorial of a number. The factorial of a number is the product of all positive integers <= the given number.
|
Factdouble |
FACTDOUBLE (number) |
FactDouble function returns the double factorial of a given value. The given value is an integer value.
|
False |
False(stringvalue) |
The False function returns the logical value for the false.
|
FDIST |
FDIST(x, degrees_freedom1, degrees_freedom2) |
Returns the F probability distribution.
|
Filterxml |
FILTERXML(xml, xpath) |
The Filterxml function returns specific data from XML content by using the specified xpath.
|
Find |
Find(lookfor, lookin, start) |
The Find finction finds a portion of a string from a particular text and returns the location of the string.
|
findb |
FINDB(find_text, within_text, [start_num]) |
FINDB locate one text string within a second text string, and return the number of the starting position of the first text string from the first character of the second text string.
|
Finv |
FINV(probability,deg_freedom1,deg_freedom2) |
The Finv function returns the inverse of the F probability distribution. If p = FDIST(x,...), then FINV(p,...) = x. Using F distribution, you can compare the degree of variability for two data sets.
|
FISHER |
FISHER(x) |
Returns the Fisher transformation at x. This transformation produces a function that is normally distributed rather than skewed.
|
FISHERINV |
FISHERINV(y) |
Returns the inverse of the Fisher transformation. If y = FISHER(x), then FISHERINV(y) = x.
|
Fixed |
Fixed ( number, decimal_places, no_commas ) |
The Fixed function rounds off to a specified number of decimal places and returns the value in text format.
|
FLOOR |
FLOOR(number, significance) |
Rounds off the given number down, toward zero, to the nearest multiple of significance.
|
FORECAST |
FORECAST(x, known_ys, known_xs) |
Calculates a future value by using existing values using a linear regression. The predicted value is a y-value for a given x-value.
|
formulatext |
FORMULATEXT (reference) |
FormulaText function returns the formula as a string.
|
FV |
FV( interest_rate, number_payments, payment, PV, Type ) |
The FV function returns the future value of an investment, based on an interest rate and a constant payment schedule.
|
fvschedule |
FVSCHEDULE(principal, schedule) |
Calculates the future value of an initial principal, after applying a series of compound interest rates.
|
GAMMA.DIST |
GAMMA.DIST(x,alpha,beta,cumulative) |
Returns the gamma distribution |
Gamma.inv |
GAMMA.INV(x,y,z,cumulative) |
The Gamma.Inv function returns the inverse of the Gamma Distribution. |
GAMMADIST |
GAMMADIST(x, alpha,beta, cumulative) |
Returns the gamma distribution.
|
Gammainv |
Gammainv(p, alpha, beta) |
The Gammainv function returns the inverse function for the GAMMADIST function.
|
GAMMAINV |
GAMMAINV(probability, alpha, beta) |
Returns the inverse of the gamma cumulative distribution. If p = GAMMADIST(x,...), then GAMMAINV(p,...) = x.
|
gammaln |
GAMMALN(x) |
Calculates the natural logarithm of the gamma function for a supplied value.
|
gammaln.precise |
GAMMALN.PRECISE(x) |
The Gammaln.Precise function returns the natural logarithm of the Gamma Distribution.
|
gcd |
GCD(number1, [number2], …) |
The GCD function returns the greatest common divisor of two or more integers. The greatest common divisor is the largest integer that goes into all given numbers without a remainder.
|
GEOMEAN |
GEOMEAN(number1, number2,...) |
Returns the geometric mean of an array or range of positive data.
|
gestep |
GESTEP(number, [step]) |
The function GESTEP tests whether a number is greater than a supplied threshold value.
|
GROWTH |
=GROWTH(known_y's, [known_x's], [new_x's],
|
This feature enables you to calculate predicted exponential growth using existing data. This calculates and returns an array of values used for the regression analysis. Growth enables you to perform a regression analysis.
|
HARMEAN |
HARMEAN(number1, number2,...)
|
Returns the harmonic mean of a data set. The harmonic mean is the reciprocal of the arithmetic mean of reciprocals.
|
hex2bin |
HEX2BIN(num, places) |
The HEX2BIN function converts a hexadecimal number into a binary number.
|
hex2dec |
HEX2DEC(number) |
The HEX2DEC function Converts a hexadecimal number to a decimal.
|
hex2oct |
HEX2OCT(num, places) |
The HEX2OCT function converts a hexadecimal number into an octal number.
|
HLOOKUP |
HLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, row_index_num, range_lookup) |
Searches for a value in the top row of the array of values and then returns a value in the same column from a row you specify in the array. Use HLOOKUP when your comparison values are located in a row across the top of a table of data and you want to look down a specified number of rows. Use VLOOKUP when your comparison values are located in a column to the left of the data you want to find.
|
HOUR |
HOUR(serial_number) |
Returns the hour of a time value. The hour is given as an integer, ranging from 0 (12:00 A.M.) to 23 (11:00 P.M.).
|
hyperlink |
HYPERLINK(linkLocation, friendlyName) |
The Hyperlink function creates a hyperlink to a document in a supplied location.
|
Hypgeom.dist
|
HYPGEOM.DIST(sample_s,number_sample,population_s,number_pop,cumulative) |
Returns the hypergeometric distribution. |
Hypgeomdist |
Hypgeomdist(sample, numberofsample, population, numberofpopulation) |
The Hypgeomdist function returns the hypergeometric distribution.
|
HYPEGEOMDIST |
HYPGEOM.DIST(sample_s,number_sample,population_s,number_pop,cumulative) |
Returns the hypergeometric distribution. HYPGEOMDIST returns the probability of a given number of sample successes, given the sample size, population successes and population size.
|
IF |
IF(logical_test, value_if_true, value_if_false) |
Returns one value if a condition you specify evaluates to True and another value if it evaluates to False. Use IF to conduct conditional tests on values and formulas.
|
iferror |
IFERROR (value, value_error) |
IfError function tests when an initial given value (or expression) returns an error, and then, this function returns a second given argument. Otherwise, the function returns the initial tested value.
|
ifna |
IFNA (Formula_value, value_if_na) |
IFNA function returns the value specified when the formula returns the #N/A error value; otherwise, it returns the result of the given formula.
|
imabs |
IMABS(inumber) |
The IMABS function returns the absolute value (the modulus) of a complex number.
|
IMAGINARY |
IMAGINARY(inumber) |
The IMAGINARY function returns the imaginary coefficient of a complex number.
|
imargument |
|
|
imconjugate |
IMCONJUGATE(inumber) |
The function IMCONJUGATE returns the complex conjugate of a complex number.
|
IMCOS |
IMCOS(inumber) |
The function IMCOS returns the cosine of a complex number
|
IMCOSH |
IMCOSH(inumber) |
The function IMCOSH returns the hyperbolic cosine of a complex number.
|
IMCOT |
IMCOT(inumber)_ |
The function IMCOT returns the cotangent of a complex number.
|
IMCOTH |
IMCOTH(number) |
The IMCOTH function returns the hyperbolic cotangent of the given complex number. For example, a given complex number "x+yi" returns "coth(x+yi)."
|
imcsc |
IMCSC(inumber) |
The function IMCSC returns the cosecant of a complex number
|
IMCSCH |
IMCSCH(inumber) |
The function IMCSCH returns the hyperbolic cosecant of a complex number.
|
IMDIV |
IMDIV(inumber1, inumber2) |
The function IMDIV returns the quotient of two supplied complex numbers.
|
IMEXP |
IMEXP(inumber) |
The function IMEXP returns the exponential of a complex number.
|
imln |
IMLN(inumber) |
The function IMLN returns the natural logarithm of a complex number.
|
IMLOG10 |
IMLOG10(inumber) |
The function IMLOG10 returns the base-10 logarithm of a complex number.
|
IMLOG2 |
IMLOG2(inumber) |
The function IMLOG2 returns the base-2 logarithm of a complex number.
|
IMPOWER |
IMPOWER(inumber, number) |
The function IMPOWER calculates a complex number raised to a supplied power.
|
IMPRODUCT |
IMPRODUCT(inumber1, [inumber2], …) |
The function IMPRODUCT returns the product of up to 255 supplied complex numbers.
|
IMREAL |
IMREAL(inumber) |
The function IMREAL function returns the real coefficient of a complex number.
|
IMSEC |
IMSEC(inumber) |
The function IMSEC returns the secant of a complex number.
|
IMSECH |
IMSECH(inumber) |
The function IMSECH returns the hyperbolic secant of a complex number.
|
IMSIN |
IMSIN(inumber) |
The function IMSIN returns the sine of a complex number.
|
IMSINH |
IMSINH(inumber) |
The function IMSINH returns the hyperbolic sine of a complex number.
|
IMSQRT |
IMSQRT(inumber) |
The function IMSQRT returns the square root of a complex number.
|
IMSUB |
IMSUB(inumber1, inumber2) |
The function IMSUB subtracts two complex numbers
|
IMSUM |
IMSUM(inumber1, [inumber2], …) |
The function IMSUM calculates the sum of two complex numbers
|
imtan |
IMTAN(inumber) |
The function IMTAN returns the tangent of a complex number.
|
IMTANH |
IMTANH(number) |
The IMTANH function returns the hyperbolic tangent of the given complex number. For example, a given complex number "x+yi" returns "tanh(x+yi)."
|
Index |
Index(range,row,col) |
The Index function returns the exact value from the provided row index and column index from a specific range.
|
Indirect |
Indirect(content) |
The Indirect function returns the reference as a string instead of providing the content or range within it.
|
info |
INFO(infoType) |
The Info function returns a text string containing information about the current operating environment.
|
INT |
INT(number) |
Rounds a number down to the nearest integer.
|
INTERCEPT |
INTERCEPT(known_y's, known_x's) |
Calculates the point at which, the least squares fit line will intersect the y-axis.
|
IPMT |
IPMT(rate, per, nper, pv, fv, type) |
Returns the interest payment for a given period for an investment based on periodic, constant payments and a constant interest rate.
|
IRR |
IRR(values, guess) |
Returns the internal rate of return for a series of cash flows represented by the numbers in values. The cash flows must occur at regular intervals such as monthly or annually.
|
IsBlank |
IsBlank( value ) |
The IsBlank function checks for blank or null values.
|
IsErr |
IsErr( value ) |
value is the value that you want to test. If the value is an error value (except #N/A), this function will return TRUE/FALSE to indicate whether a value is an error.
|
ISERROR |
ISERROR(value) |
Returns True if the value is a string that starts with a #.
|
iseven |
ISEVEN (value) |
The ISEVEN function returns TRUE if given number is an even number and returns FALSE if the given number is an odd number.
|
isformula |
ISFORMULA (reference) |
The IsFormula function returns true or false when there is a reference to a cell that contains a formula.
|
IsLogical |
IsLogical( value ) |
The IsLogiacl function checks whether a value is a logical value and returns a TRUE or FALSE.
|
IsNA |
IsNA(value) |
The IsNA function returns a boolean value after determining that the provided value is a #NA error value.
|
IsNonText |
IsNonText(text) |
The IsNonText function returns the boolean value after determining that the provided value is not a string.
|
ISNUMBER |
ISNUMBER(value) |
Returns True if the value parses as a numeric value.
|
isodd |
ISFORMULA (reference) |
IsOdd function returns true when the given number is an odd number and returns false when the given number is even.
|
isoweeknum |
ISOWEEKNUM( DateTime) |
For a given date, the ISOWeekNum function returns the ISO week number of that year.
|
ISPMT |
ISPMT(rate, per, nper, pv) |
Calculates the interest paid during a specific period of an investment.
|
isref |
ISREF(given_value) |
The ISREF function returns the logical value TRUE if the given value is a reference value; otherwise, the function returns FALSE.
|
IsText |
IsText(text) |
The IsText function returns a boolean value after determining that the provided value is a string.
|
jis |
JIS(text) |
The JIS function converts single byte characters into double byte characters in a text string.
|
KURT |
KURT(number1, number2, ...) |
Returns the kurtosis of a data set. Kurtosis characterizes the relative peakedness or flatness of a distribution compared with the normal distribution. Positive kurtosis indicates a relatively peaked distribution. Negative kurtosis indicates a relatively flat distribution.
|
LARGE |
LARGE(array, k) |
Returns the k-th largest value in a data set.
|
lcm |
LCM(number1, [number2], …) |
THe LCM function returns the least common multiple of integers. The least common multiple is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of all given numbers.
|
LEFT |
LEFT(text, num_chars) |
LEFT returns the first character or characters in a text string, based on the number of characters you specify.
|
leftb |
LEFTB(text, bytes) |
The LEFTB function calculates the first character or characters in a text string, based on the number of bytes you specify.
|
LN |
LN(number) |
Returns the natural logarithm of a number. Natural logarithms are based on the constant e (2.718281828459...).
|
LEN |
Len(text) |
LEN returns the length of a text string, including spaces.
|
LenB |
LENB(name) |
The LENB function returns the number of bytes used to represent the characters in a text string.
|
LOG |
LOG(number, base) |
Returns the logarithm of a number to the base that you specify.
|
LOG10 |
LOG10(number) |
Returns the base-10 logarithm of a number.
|
LOGEST |
=LOGEST(known_y's, [known_x's], [const], [stats]) |
This feature enables you to calculate predicted exponential growth using existing data. This calculates and returns an array of values used for the regression analysis. Logest calculates and returns an array of values that is used in regression analysis.
|
LOGINV |
LOGINV(probability, mean, standard_dev) |
Returns the inverse of the lognormal cumulative distribution function of x, where ln(x) is normally distributed with parameters mean and standard_dev. If p = LOGNORMDIST(x,...), then LOGINV(p,...) = x.
|
LOGNORM.DIST |
LOGNORM.DIST(x,mean,stdev,cumulative) |
The Lognorm.Dist function calculates the Log-Normal Probability Density Function or the Cumulative Log-Normal Distribution Function for a supplied value of x.
|
LOGNORM.inv
|
LOGNORM.INV(probability, mean, stdev) |
The Lognorm.Inv function calculates the inverse of the Cumulative Log-Normal Distribution Function of x for a supplied probability.
|
LOGNORMDIST |
LOGNORMDIST(x, mean, standard_dev) |
Returns the cumulative lognormal distribution of x, where ln(x) is normally distributed with parameters mean and standard_dev.
|
Lower |
Lower( text ) |
The Lower function converts all characters in the specified text string to lowercase. Characters in the string that are not letters, are not changed.
|
Match |
Match( value, array, match_type ) |
The Match function searches for a specified value in an array and returns the relative position of that item.
|
MAX |
MAX(number1, number2, ...) |
Returns the largest value in a set of values.
|
MAXA |
MAXA(value1, value2, ...) |
Returns the largest value in a list of arguments. Text and logical values such as True and False are compared as well as numbers.
|
MEDIAN |
MEDIAN(number1, number2, ...) |
Returns the median of the given numbers. The median is the number in the middle of a set of numbers; that is, half the numbers have values that are greater than the median and half have values that are less.
|
MID |
MID(text, start_position, num_chars) |
MID returns a text segment of a character string. The parameters specify the starting position and the number of characters.
|
midb |
MIDB(text, startNum, numBytes) |
The MIDB function returns a specific number of characters from a text string, starting at the position you specify, based on the number of bytes you specify.
|
MIN |
MIN(number1, number2, ...) |
Returns the smallest number in a set of values.
|
MINA |
MINA(value1, value2, ...) |
Returns the smallest value in the list of arguments. Text and logical values such as True and False are compared as well as numbers.
|
MINUTE |
MINUTE(serial_number) |
Returns the minutes of a time value. The minute is given as an integer, ranging from 0 to 59.
|
MIRR |
MIRR(values, finance_rate, reinvest_rate) |
Returns the modified internal rate of return for a series of periodic cash flows.
|
MOD |
MOD(number, divisor) |
Returns the remainder after the number is divided by a divisor. The result has the same sign as the divisor.
|
MODE |
MODE(number1, number2, ...) |
Returns the most frequently occurring or repetitive, value in an array or range of data.
|
MONTH |
MONTH(serial_number) |
Returns the month of a date represented by a serial number. The month is given as an integer, ranging from 1 (January) to 12 (December).
|
mround |
MROUND(number, multiple) |
THe MROUND function rounds a number up or down, depending on the nearest multiple of given number.
|
multinomial |
MULTINOMIAL(number1, [number2], …) |
THe MULTINOMIAL function calculates the ratio of the factorial of a sum of values to the product of factorials of those values.
|
n |
N (value) |
The N function converts the given value into a numeric value.
|
na |
NA() |
The NA function returns the #N/A error. This error message is produced when a formula is unable to find a value that it needs. This error message denotes ‘value not available’.
|
NEGBINOM.DIST
|
NEGBINOM.DIST(F_number,S_number,S_probability,cumulative) |
The Negbinom.Dist function calculates the probability mass function or the cumulative distribution function for the Negative Binomial Distribution.
|
NETWORKDAYS.INTL |
NETWORKDAYS.INTL(startDate, endDate) |
NETWORKDAYS.INTL calculates the number of whole work days between two supplied dates.
|
NEGBINOMDIST |
NEGBINOMDIST(number_f, number_s, probability_s) |
Returns the negative binomial distribution. NEGBINOMDIST returns the probability that there will be number_f failures before the number_s-th success, when the constant probability of a success is probability_s.
|
Norm.dist |
NORM.DIST(x,mean,stdev,cumulative) |
The NORM.DIST function calculates the normal distribution for a supplied value of x, and a supplied distribution mean & standard deviation.
|
norm.inv |
NORM.INV(probability,mean,standard_dev) |
Returns the inverse of the normal cumulative distribution
|
NORM.S.DIST |
NORM.S.DIST(val, cumulative) |
The Norm.S.Dist function returns the standard normal distribution.
|
NORM.S.INV |
NORM.S.INV(probability) |
The Norm.S.Inv function returns the inverse of the standard normal cumulative distribution.
|
NORMDIST |
NORMDIST(x, mean, standard_dev, cumulative) |
Returns the normal distribution for the specified mean and standard deviation.
|
NORMINV |
NORMINV(probability, mean, standard_dev) |
Returns the inverse of the normal cumulative distribution for the specified mean and standard deviation.
|
NormsDist |
NormsDist(value) |
The NormsDist function returns the probability that the observed value of a standard normal random variable will be less than or equal to the parameter.
|
NormsInv |
NormsInv(value) |
The NormsInv function returns the standard normal random variable that has Mean 0 and Standard Deviation 1
|
NOT |
NOT(logical) |
Reverses the value of its argument.
|
NOW |
NOW( ) |
Returns the serial number of the current date and time.
|
NPER |
NPER(rate, pmt, pv, fv, type) |
Returns the number of periods for an investment based on periodic, constant payments and a constant interest rate.
|
NPV |
NPV(rate, value1, value2, ...) |
Calculates the net present value of an investment by using a discount rate and a series of future payments (negative values) and income (positive values).
|
numbervalue |
NUMBERVALUE(text) |
The NumberValue function converts text to a number in a locale-independent way.
|
oct2bin |
OCT2BIN(number, [places]) |
The OCT2BIN function Converts octal number to binary.
|
oct2dec |
OCT2DEC(number) |
The OCT2DEC function Converts octal number to a decimal.
|
OCT2HEX |
OCT2HEX(number, [places]) |
The OCT2HEX function Converts octal number to hexadecimal.
|
ODD |
ODD(number) |
Returns the number rounded up to the nearest odd integer.
|
Offset |
Offset( range, rows, columns, height, width ) |
The Offset function returns a reference to a range that is offset a number of rows and columns from any given range or cell.
|
OR |
OR(logical1, logical2, ...) |
Returns True if any argument is True; returns False if all arguments are False.
|
PEARSON |
PEARSON(array1, array2) |
Returns the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient, r, a dimensionless index that ranges from -1.0 to 1.0 inclusive and reflects the extent of a linear relationship between two data sets.
|
PERCENTILE |
PERCENTILE(array, k) |
Returns the k-th percentile of values in a range.
|
PERCENTILE.exc |
PERCENTILE.EXC(array, k) |
The Percentile.Exc function returns the k-th percentile of values in a range, where k is in the range of 0 to 1 exclusively.
|
PERCENTILE.inc
|
PERCENTILE.INC (array,k)
|
The Percentile.Inc function returns the k-th percentile of values in a range, where k is in the range 0 to 1.
|
PERCENTRANK |
PERCENTRANK(array, x, significance) |
Returns the rank of a value in a data set as a percentage of the data set.
|
PERCENTRANK.exc
|
PERCENTRANK.EXC(array,x,[significance]) |
Returns the rank of value in dataset as a percentage of the data set as percentage (0….1, exclusive) of the dataset
|
PERCENTRANK.inc
|
PERCENTRANK.INC(array,x,[significance]) |
Returns the rank of value in dataset as a percentage of the data set as percentage (0….1, inclusive) of the dataset
|
Permut |
Permut(n, k) |
The Permut function returns the number of permutations of n items taken at k time.
|
permutationa |
PERMUTATIONA(number, number-chosen) |
The PermutationA function returns the number of permutations for a given number of objects (with repetitions) that can be selected from the total number of objects.
|
PI |
PI( ) |
Returns the number 3.14159265358979, the mathematical constant pi, accurate to 15 digits.
|
PMT |
PMT(rate, nper, pv, fv, type) |
Calculates the payment for a loan based on constant payments and a constant interest rate.
|
POISSON |
POISSON(x, mean, cumulative) |
Returns the Poisson distribution.
|
POISSON.dist |
POISSON.DIST(x,mean,cumulative) |
The Poisson.Dist function calculates the Poisson Probability Mass Function or the Cumulative Poisson Probability Function for a supplied set of parameters.
|
Pow |
POW(number, power) |
The Pow function returns the result of a number raised to a power.
|
POWER |
POWER(number, power) |
Returns the result of a number raised to a power.
|
PPMT |
PPMT(rate, per, nper, pv, fv, type) |
Returns the payment on the principal for a given period, for an investment based on periodic, constant payments and a constant interest rate.
|
PROB |
PROB(x_range, prob_range, lower_limit, upper_limit) |
Returns the probability whose values are in a range that is between two limits. If upper_limit is not supplied, returns the probability that values in x_range are equal to lower_limit.
|
PRODUCT |
PRODUCT(number1, number2, ...) |
Multiplies all the numbers given as arguments and returns the product.
|
proper |
PROPER(text) |
The Proper function changes the first letter of text into a capital letter and following letters changes to lowercases.
|
PV |
PV(rate, nper, pmt, fv, type) |
Returns the present value of an investment. The present value is the total amount that a series of future payments is worth now.
|
QUARTILE |
QUARTILE(array, quart) |
Returns the quartile of a data set.
|
quotient |
QUOTIENT(numerator, denominator) |
THe QUOTIENT function calculates the integer portion of a division. This function is used to discard the remainder of a division.
|
RADIANS |
RADIANS(angle) |
Converts degrees to radians.
|
RAND |
RAND( ) |
Returns an evenly distributed random number greater than or equal to 0 and less than 1.
|
Randbetween |
RANDBETWEEN(bottom, top) |
THe RANDBETWEEN function returns a random integer number between given numbers. A new random integer number is returned each time when worksheet is recalculated.
|
RANK |
RANK(number, ref, order) |
Returns the rank of a number in a list of numbers. The rank of a number is its size relative to other values in a list. (If you were to sort the list, the rank of the number would be its position.)
|
RATE |
RATE(nper, pmt, pv, fv, type, guess) |
Returns the interest rate per period of an annuity. RATE is calculated by iteration and may not converge to a unique solution.
|
received |
RECEIVED(settlement, maturity, investment, discount, [basis]) |
Calculates the amount received at maturity for a fully invested Security
|
REPLACE |
REPLACE(oldText, startNum, numChars, newText) |
The Replace function replaces a certain part of text with a different part of text based on the number of characters given.
|
REPLACeb |
REPLACEB(old_text, start_num, num_bytes, new_text) |
REPLACEB replaces part of a text string, based on the number of bytes you specify, with a different text string.
|
rept |
REPT(string, number) |
The Rept function returns a supplied text string, repeated a specified number of times.
|
RIGHT |
RIGHT(text, num_chars) |
RIGHT returns the last character or characters in a text string, based on the number of characters you specify.
|
RIGHTb |
RIGHTB(string, num_bytes) |
The RIGHTB function returns the last character or characters in a text string, based on the number of bytes.
|
roman |
ROMAN(number, [form]) |
THe ROMAN function converts an Arabic numeral to roman numeral as text.
|
ROUND |
ROUND(number, num_digits) |
Rounds a number to a specified number of digits.
|
ROUNDDOWN |
ROUNDDOWN(number, num_digits) |
Rounds a number down towards zero.
|
ROUNDUP |
ROUNDUP(number, num_digits) |
Rounds a number up away from 0 (zero).
|
rri |
RRI(nper, pv, fv) |
Calculates an equivalent interest rate for the growth of an investment
|
RSQ |
RSQ(known_y's, known_x's) |
Returns the square of the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient through data points in known_y's and known_x's.
|
search |
SEARCH(findText,withinText, startNum)_ |
The Search function finds one text string (find_text) within another text string (within_text), and returns the number of the starting position of find_text.
|
searchb |
SEARCHB(findText,withinText, startNum)_ |
The SEARCHB function returns the position of a specified character or sub-string within a given text string.
|
sec |
SEC(number) |
The Sec function returns the secant of an angle.
|
sech |
SECH(number) |
The SECH function returns the hyperbolic secant of an angle.
|
SECOND |
SECOND(serial_number) |
Returns the seconds of a time value. The second is given as an integer in the range 0 (zero) to 59.
|
seriessum |
SERIESSUM(x, n, m, coefficients) |
Returns the sum of a power series based on the formula: SERIESSUM(x, n, m, a) = a1*x^n + a2*x^(n+m)+ai*x^(n+(i-1)*m)
|
SIGN |
SIGN(number) |
Determines the sign of a number. Returns 1 if the number is positive, zero (0) if the number is 0 and -1 if the number is negative. |
SIN |
SIN(number) |
Returns the sine of the given angle.
|
SinH |
SinH(value) |
The SinH function computes the hyperbolic sine of the argument.
|
SKEW |
SKEW(number1, number2, ...) |
Returns the skewness of a distribution. Skewness characterizes the degree of asymmetry of a distribution around its mean.
|
skew.p |
SKEW.P(number 1, [number 2],…) |
Returns the skewness of a distribution
|
SLN |
SLN(cost, salvage, life) |
Returns the straight-line depreciation of an asset for one period.
|
SLOPE |
SLOPE(known_y's, known_x's) |
Returns the slope of the linear regression line through data points in known_y's and known_x's. The slope is the rate of change along the regression line.
|
SMALL |
SMALL(array, k) |
Returns the k-th smallest value in a data set.
|
SQRT |
SQRT(number) |
Returns a positive square root.
|
sqrtpi |
SQRTPI(number) |
THe SQRTPI function returns the square root of a given number multiplied by the mathematical constant, π.
|
STANDARDIZE |
STANDARDIZE(x, mean, standard_dev) |
Returns a normalized value from a distribution characterized by mean and standard_dev.
|
STDEV |
STDEV(number1, number2, ...) |
Estimates the standard deviation based on a sample. The standard deviation is a measure of how widely values are dispersed from the average value (the mean).
|
STDEV.p |
STDEV.P(number1,[number2],…]) |
The STDEV.P function calculates the standard deviation of a supplied set of values.
|
stdev.s |
STDEV.s(number1,[number2],…]) |
The STDEV.S function calculates the sample standard deviation of a supplied set of values.
|
STDEVA |
STDEVA(value1, value2 , ...) |
Estimates standard deviation based on a sample. The standard deviation is a measure of how widely values are dispersed from the average value (the mean). Text and logical values such as True and False are also included in the calculation.
|
STDEVP |
STDEVP(number1, number2, ...) |
Calculates standard deviation based on the entire population given as arguments.
|
STDEVPA |
STDEVPA(value1, value2, ...) |
Calculates the standard deviation based on the entire population given as arguments, including text and logical values.
|
STEYX |
STEYX(known_y's, known_x's) |
Returns the standard error of the predicted y-value for each x in the regression.
|
SUBSTITUTE |
SUBSTITUTE(text, old_text, new_text, instance_num) |
Substitutes new_text for old_text in a text string. Use SUBSTITUTE when you want to replace specific text in a text string; use REPLACE when you want to replace any text that occurs in a specific location in a text string.
|
subtotal |
SUBTOTAL (function_Number, ref1, (ref2)…) |
Subtotal function returns a subtotal in a list. Once the subtotal list is created, you can modify it by editing the Subtotal function.
|
Sum |
Sum( number1, number2, ... number_n ) |
The Sum function adds all numbers in a range of cells and returns the result.
|
SumIf |
SumIf( range, criteria, sum_range ) |
SumIf function adds the specified range of cells by a given criteria.
|
SUMPRODUCT |
SUMPRODUCT(array1, array2, array3, ...) |
Multiplies corresponding components in the given arrays and returns the sum of those products.
|
SUMSQ |
SUMSQ(number1, number2, ...) |
Returns the sum of the squares of the arguments.
|
SumXmY2 |
SumXmY2( array1, array2 ) |
The SumXmY2 function calculates the sum of the squares of the differences between the corresponding items in the arrays and returns the sum as results.
|
SUMX2MY2 |
SUMX2MY2(array_x, array_y) |
Returns the sum of the difference of squares of corresponding values in two arrays.
|
SUMX2PY2 |
SUMX2PY2(array_x, array_y) |
Returns the sum of the sum of squares of corresponding values in two arrays. The sum of the sum of squares is a common term in many statistical calculations.
|
SYD |
SYD(cost, salvage, life, per) |
Returns the sum-of-years' digits depreciation of an asset for a specified period.
|
t |
T( value ) |
The T function tests whether the given value is a text or not. When the given value is a text, then it returns the given text. Otherwise, the function returns as an empty text string.
|
t.dist |
T.DIST(x,deg_freedom,tails) |
The T.Dist returns the Percentage Points (probability) for the Student t-distribution where a numeric value (x) is a calculated value of t for which the Percentage Points are to be computed.
|
t.inv |
T.INV(probability,deg_freedom) |
The T.INV returns the left-tailed inverse of the Student’s t-distribution.
|
TAN |
TAN(number) |
Returns the tangent of a number.
|
TANH |
TANH(number) |
Returns the hyperbolic tangent of a number.
|
TEXT |
TEXT(value, format_text) |
Converts a value to text in a specific number format.
|
TIME |
TIME(hour, minute, second) |
Returns the decimal number for a particular time. The decimal number returned by TIME is a value ranging from 0 (zero) to 0.99999999, representing the times from 0:00:00 (12:00:00 A.M.) to 23:59:59 (11:59:59 P.M.).
|
TIMEVALUE |
TIMEVALUE(time_text) |
Returns the decimal number of the time represented by a text string. The decimal number is a value ranging from 0 (zero) to 0.99999999, representing the times from 0:00:00 (12:00:00 A.M.) to 23:59:59 (11:59:59 P.M.).
|
TODAY |
TODAY( ) |
Returns the serial number of the current date. The serial number is the number of days since Jan 1, 1900.
|
Trim |
Trim( text ) |
The Trim function returns a text value with the leading and trailing spaces removed.
|
TRIMMEAN |
TRIMMEAN(array, percent) |
Returns the mean of the interior of a data set. TRIMMEAN calculates the mean taken by excluding a percentage of data points from the top and bottom tails of a data set.
|
True |
True(stringvalue) |
The True function returns the logical value for True.
|
TRUNC |
TRUNC(number, num_digits) |
Truncates a number to an integer by removing the fractional part of the number.
|
Type |
TYPE( value ) |
The TYPE function receives a value and returns an integer that represents the supplied value’s data type.
|
unchar |
UNICHAR(num) |
The Unichar function retrieves the Unicode character for a given numeric value.
|
unicode |
UNICODE(text) |
The UNICODE function calculates the number corresponding to the first character of the text.
|
Upper |
Upper( text ) |
The Upper function converts all characters in a text string to uppercase.
|
Value |
Value(range) |
The Value function computes the date or a string that contains the number, and converts it into number format.
|
Var |
Var( number1, number2, ... number_n ) |
The Var function returns the variance of a population based on sample of numbers.
|
VarA |
VarA( value1, value2, ... value_n ) |
The VarA function returns the variance of a population based on a sample of numbers, text, and logical values (ie: TRUE or FALSE).
|
VarP |
VarP(listofvalues) |
The VarP function returns population variance of the listed values.
|
VARPA |
VARPA(value1, value2, ...) |
Calculates variance based on the entire population. In addition to numbers and text, logical values such as True and False are also included in the calculation.
|
VDB |
VDB(cost, salvage, life, start_period, end_period, factor, no_switch) |
Returns the depreciation of an asset for any period you specify, including partial periods, using the double-declining balance method or some other method you specify. VDB stands for variable declining balance.
|
VLOOKUP |
VLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, range_lookup) |
Searches for a value in the left most column of a table and then returns a value in the same row from a column you specify in the table. Use VLOOKUP instead of HLOOKUP when your comparison values are located in a column to the left of the data you want to find.
|
webservice |
WEBSERVICE(url) |
The Webservice function returns data from a web service on the Internet or Intranet.
|
WEEKDAY |
WEEKDAY(serial_number,return_type) |
Returns the day of the week corresponding to a date. The day is given as an integer, ranging from 1 (Sunday) to 7 (Saturday) by default.
|
Weeknum |
WEEKNUM( serialNum, [returnType] ) |
For a supplied a date, the WEEKNUM function returns an integer representing the week number (from 1 to 53) of the year.
|
Weibull |
WEIBULL(x,alpha,beta,cumulative) |
The Weibull function returns the Weibull distribution. This distribution is used in reliability analysis, such as calculating a device's mean time to failure.
|
Weibull.dist
|
WEIBULL.DIST(x,alpha,beta,cumulative) |
The Weibull.Dist function returns the Weibull Distribution.
|
workday |
WORKDAY(startDate, Days, [holidays]) |
The Workday function returns a date that is a supplied number of working days (excluding weekends and holidays) ahead of a given start date.
|
workday.intl |
WORKDAY.INTL (startDate, days, [weekend], [holidays]) |
The WORKDAY.INTL function returns a date that is a supplied number of working days (excluding weekends and holidays) ahead of a given start date.
|
Xirr |
Xirr(cashflow, datelist, value) |
The Xirr function computes the internal rate of return for a schedule of possibly non-periodic cash flows.
|
xor |
XOR (logical_value1, logical_value2…) |
XOR function returns the exclusive OR for the given arguments.
|
YEAR |
YEAR(serial_number) |
Returns the year corresponding to a date. The year is returned as an integer in the range 1900-9999.
|
yearfrac |
YEARFRAC(start_date, end_date, [basis]) |
YEARFRAC calculates the fraction of the year represented by the number of whole days between two dates (the start_date and the end_date). For instance, you can use YEARFRAC to identify the proportion of a whole year's benefits, or obligations to assign to a specific term.
|
Z.TEST |
Z.TEST(array,x,[sigma]) |
Returns the one-tailed P-value of a z-test. For a given hypothesized population mean, x, Z.TEST returns the probability that the sample mean would be greater than the average of observations in the data set (array) — that is, the observed sample mean. To see how Z.TEST can be used in a formula to compute a two-tailed probability value, see the Remarks section below.
|
ZTEST |
ZTEST(array, u0, sigma) |
Returns the one-tailed probability-value of a z-test.
|